WHAT IS AN ONLINE ACCOUNTING DEGREE?
Online accounting degree programs are not any different from a program you would attend on campus. While you study in an accounting program, you would start by learning basic accounting principles. This may include how prepare and examine financial records. Also, how to track financial transactions. As well as how to ensure that financial documents are accurate and thorough.
Also, you may learn how to check whether income taxes are paid properly and on time. And, learn about business law and important tax laws.
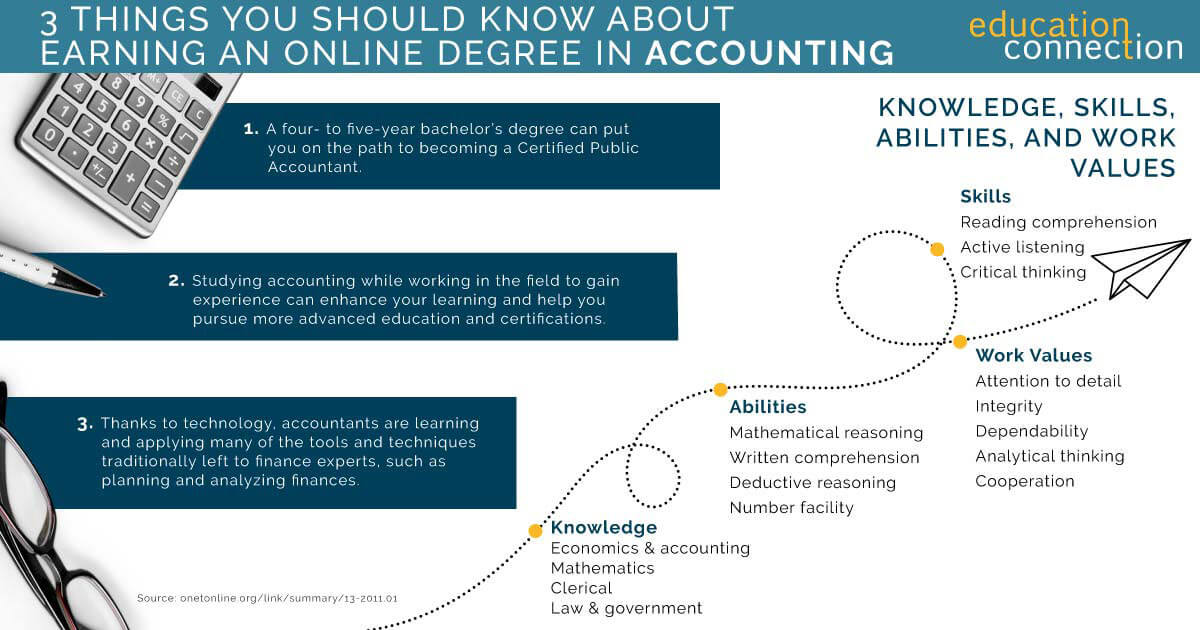
What will you need to be employed in this field? Well, these careers will require you to be good at counting numbers as well as basic decision making. You also need to be able to track money. And, you should understand financial management. Work experience in forecasting and analysis is also desirable. Additionally, internal control and consulting could be areas you pursue. What do all of these options mean for you? Well, it means that as an accountant today, you must develop a range of knowledge and skills. Thus, online accounting degrees could be a great option for you.
TYPES OF ONLINE ACCOUNTING DEGREE PROGRAMS
Associates Degree in Accounting
Are you looking to learn the basics? Well, an A.S. in Accounting is designed to equip you with that. Here, you will come away with a variety of basic accounting skills. And, you will find these skills to be useful in entry level accounting positions.
You will cover:
- Record patient history
- Answer telephones
- Arrange lab services
- Enter & update health records
- Schedule appointments
- Measure vital signs
Bachelor’s Degree in Accounting
In this program, you will learn accountancy. You will also study financial and budgeting basics. In addition, you could cover the underlying forces that drive organizations.
What you will commonly study:
- Financial and managerial accounting
- Cost accounting
- Advanced accounting
- Federal tax
- Financial statement analysis
- Auditing
Masters Degree in Accounting
f you are a business student, this program will help you develop your core knowledge of accounting. It will also help you pursue licensure as an accountant. You may use electives to focus your studies in a specific area of accounting. Through the program, you will study for the CPA exam. And, you will also develop networks.
Additionally, you could cover:
- Accounting and information systems
- Auditing
- Financial accounting theory
- Ethics in accounting
- Case studies and research in accounting
- Leadership in accounting
ONLINE ACCOUNTING DEGREE PROGRAMS
By earning a bachelor’s degree, you could develop your mathematical skills. In addition, you may be able to boost your financial, and social knowledge. Generally, the more advanced your degree, the more you will learn. When looking for an accounting program you will also find that sometimes it is part of the business school, while other times it is a liberal arts program. If it is a business school program be sure it is accredited by the ACBSP.
- In a two year associate degree, you will learn the basics. You will also develop your reading and writing skills. Your speaking skills could see a boost, too. This is because you will take several general education courses.
- If you pursue a four year online bachelor of science in accounting, you will learn the basics of accounting as well. Plus, you will study a specific area of accounting. For example, you could study nonprofit accounting. Or, you could study energy economics. Are you interested in investment? You could take that on. You will also spend time developing your reading, writing, and speaking skills. And, you will work on your critical thinking skills.
- With a two year M.S. degree in accounting, you will broaden your existing accounting knowledge. You will further focus it on a specific area of accounting. Through accounting focused course work, you will further advance your professional skills. You will also conduct research, which will help you across the board. In addition, you will enhance your social skills.
1
Southern New Hampshire University
- Take advantage of some of the nation’s most affordable tuition rates, while earning a degree from a private, nonprofit, NEASC accredited university
- Qualified students with 2.5 GPA and up may receive up to $20K in grants & scholarships
- Multiple term start dates throughout the year. 24/7 online classroom access.
Popular Programs
Business Administration, Psychology, Information Technology, Human Services…
2
University of Arizona Global Campus
- 99% of University of Arizona Global Campus students study online
- University of Arizona Global Campus offers affordable tuition, so college is accessible to many students.
- he University of Arizona Global Campus (formerly Ashford University) is accredited by WASC Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC)
Available Programs
Accounting and Finance, Information Technology, Political Science…
3
Western Governors University
- Award-winning programs created to help you succeed.
- A quality education doesn’t have to be expensive. Earn an accredited degree for less.
- Programs start monthly – Apply free this week!
Sponsored Schools
WHAT DO ACCOUNTING COURSES LOOK LIKE?
So, are you wondering what you will study in an online accounting degree program? Well, you could specialize in different accounting majors. Let’s get you acquainted with some of the paths you could take.
Have you heard of managerial accounting? In managerial accounting, you would use the provisions of accounting information to better inform what matters to a business. This information is then used to make better business decisions. You will also find it boosts your performance of control functions.
Or, you could study public accounting. On this track, you would likely work at an accounting firm. As a public accountant, you would provide accounting expertise. Additionally, you could provide auditing, and tax services to your clients. This, you will find, can include the handling of many accounting tasks. You would likely work on an consulting basis. Or, you could find yourself auditing the financial statements of clients.
Tax accounting is another area you could specialize in. What would you do in this role? As a tax accountant, you would need to understand the tax reporting requirements. You would essentially prepare tax returns. You could work with individuals. Or, you could work with businesses. Additionally, you could provide highly complex tax planning services for multinational corporations.
Have you heard of forensic accounting? Are you interested in white collar crime? Well, if you pursue forensic accounting, you would often encounter it. In this role, you would combine accounting with investigative techniques you would learn. You would then utilize these tactics to discover financial crimes. As a forensic accountant, one of your key functions is explaining the nature of a financial crime to the courts.
Some common accounting courses include:
Principles of Finance: This course could introduce you to finance. You may learn the true value of money and what makes U.S. businesses different from foreign businesses.
Financial and Managerial Accounting: Learn how managers use financial data to make decisions. Subjects may include how companies manage money and try to control spending.
Cost Accounting: Companies want to know how every dollar is spent. You may learn the systems that accountants use to show exactly where the money goes.
Accounting Principles: First, you may learn about how to run a business and make decisions. Then, you could learn accounting concepts and how to write financial reports.
Federal Taxation: You may learn how federal taxes affect people and companies. And, you could also learn research methods and the correct way to report taxes.
Financial Statement Analysis: This course aims to show how to analyze financial statements. You may also learn the difference between money and income and how prices are set.
Auditing: You may learn to research data about a person or company. Your research could prove that rules are being followed or money is being spent correctly.
Ethics in Accounting: In this course could help you find out if a business is being run fairly. You may examine how politics, laws, technology and hiring practices affect businesses.
HOW LONG DOES IT TAKE TO COMPLETE AN ONLINE ACCOUNTING DEGREE PROGRAM?

ACCOUNTING CAREER PATHS
Are you wondering what you would actually do as an accountant? Who would you work for? Once you earn a degree in accounting you could do many things. For example, you could become an auditor. Or, you could become a public accountant, or a corporate accountant. In addition, you could become a forensic accountant. And, you could even become a tax examiner. And, you could pursue a path as a revenue agent. You could do this work for individuals. But, you could also work with families. Or you could consult with businesses, and other organizations.
For example, you could work with nonprofits. Or, you could consult with government entities. Did you know that 23% of accountants work for entities that provide accounting, tax preparation, bookkeeping, and payroll services? You can find another 8% split evenly between government entities and finance and insurance agencies. In addition, you will find that 6% are split evenly between working in management and being self employed. You will find these roles account (no pun intended) for the highest employment rates of accountants.
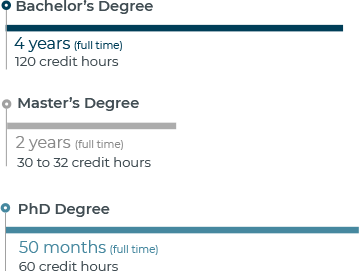
Are you wondering what you need to be qualified? Well, you will find that some individuals and businesses will hire you if you have an A.S. degree. Or, you could have a certificate. However, the majority of employers will be more likely to hire you if you have at least a B.S. degree. How long will that take you? Well, you can plan on studying for at least four years before becoming an accountant. Becoming a CPA will take you longer.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FINANCE AND ACCOUNTING?
You may have heard that accounting is one part of finance. In accounting, you will deal primarily with recording and reporting on financial transactions. In finance, however, you will primarily deal with planning and directing those financial transactions. Let’s break it down for you. In accounting, you will track the money that comes in and goes out of a company or entity. But in finance, you will cover the broader management of money.
You would also cover assets and liabilities. In finance, you make plans for present day protection. And you also plan for future growth. Another thing you should be acquainted with, is the trends in today’s financial world. Importantly, you will find that software and technology handle many of the tasks. And, you can guess that these tasks were historically assigned to accountants. Because of this, as an accountant nowadays, you will need to develop your skill set broadly. This means you should learn all you can in other areas. These areas, you will find, were more traditionally assigned to experts in finance.
THE AVERAGE COST OF A BACHELOR’S DEGREE IN ACCOUNTING
Are you wondering about cost? Let’s go over what you will pay for an online accounting degree. For one thing, you will find the cost of earning an online bachelor’s degree varies. You must consider the school. You will also find that it varies by the number of credits per program. Sometimes, you will find, it varies by state. However, you can gain a sense of what you would pay for a four year degree in accounting across the country, below. Also, you can see the institution type. You will find that, according to IPEDS, the median in state tuition at a public school is 6,892 for a B.S. in Accounting. The median out of state tuition at a private institution, you can see, is $32,084.
| School | # of Credits Required | Cost Per Credit | Total Tuition Cost |
| Colorado State U Global Campus | 120 | $350 | $42,000 |
| American Intercontinental U | 180 | $325 | $58,500 |
| Ashford U | 120 | $485 | $58,200 |
CERTIFICATIONS AND LICENSES AN ONLINE BACHELOR’S IN ACCOUNTING PREPARES YOU FOR
Earning an online Bachelor’s in Accounting may help you meet education requirements for certain certs and licenses. Online students should check with their programs to learn if they are suitable for goals like pursuing a CPA license. Here are some certs to learn more about:
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA). To earn this credential, you need 150 semester hours of college credit. Since that is 30 hours more than the usual 4 year Bachelor’s degree program, you’ll need to earn the extra credits. Some do that by earning a Master’s degree. But, that may not be necessary. You’ll also need to pass a national exam. And, meet other state requirements.
- Certified Management Accountant (CMA). Applicants must hold a Bachelor’s degree. They must have two years of work experience in management accounting. And, pass a two part exam and agree to pursue a certain amount of continuing education. They must also comply with professional conduct standards.
- Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE). This fraud examination credential may be ideal for those in the business world, government, or law enforcement. Usually, you need a minimum of a Bachelor’s degree. And, two years of work experience in the detection or deterrence of fraud. Though, there may be ways around these prereqs. You must also pass the CFE exam. It covers Financial Transactions and Fraud Schemes, Law, Investigation, and more.
PROFESSIONAL ACCOUNTING ORGANIZATIONS
Some members of the accounting field join professional orgs. This could be a great way to network, learn, and grow as an accounting pro. Here are a few orgs to know about.
- American Accounting Association (AAA). This is a group for accountants in academia. It focuses on research, problem solving, and more. Though many members are researchers, practitioners, or faculty members, AAA offers different memberships. One is a pathway option for undergrad students.
- American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA).This is an org for CPAs. AICPA certifies CPAs and also offer memberships for students and non CPAs. Potential benefits to joining include professional development, resources, community, and more.
- Institute of Management Accountants (IMA).This org awards the CMA or Certified Management Accountant credential. Through IMA, you can pursue continuing education and keep learning throughout your career. You could also network with other CMAs. And, pursue professional development.
- The National Society of Accountants (NSA). This membership org is aimed at “Main Street” accountants. These include CPAs, those who own tax and accounting firms, and others. Members enjoy info resources, discounts on services you could use in your practice, and a lot more.
- International Federation of Accountants (IFAC). This is a global org serving 130 countries. Including the United States. It has 170 professional accountancy organizations (PAOs) around the world. IFAC offers resources and support. Members can share ideas for improving the accounting profession at a global level.
HOW DO YOU QUALIFY TO TAKE THE CPA EXAM?
To take the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) exam, you must log 150 credit hours of education in accounting. You can earn this number of credits in the following ways:
- You can pursue a four year B.S. program in accounting. Plus you can take one year of an M.S. program in accounting.
- Earning an accelerated four year B.S. degree that allows you to earn 150 credit hours.
- You can pursue a four year B.S. degree in accounting. Then, you can earn 30 credit hours of non degree education in accounting.
If you want to become a CPA, you should talk to an advisor in your accountant degree program. You can discuss what you need to do to earn 150 credit hours. Also, you may learn about the CPA exam through the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). As you can gather, they are the organization that manages the exam.
WHAT IS A CPA?
As a CPA, you are a certified to the public. In other words, you are an accountant who is licensed by your state’s Board of Accountancy. If you have this designation, it demonstrates that you have professional competence. You will be marketable in your specialized field of accounting or auditing. Unlike unlicensed accountants, as a CPA, you can file reports with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
If you pass the CPA exam and become licensed, it also qualifies you to secure additional certs. Some certs you could earn are: Accredited in Business Valuation, Certified Information Technology Professional, or Personal Financial Specialist. Gaining these certificates may require you to pursue additional education. You may also need more experience. And you could need to pass other exams.
As an accountant, you must log 150 credit hours to be eligible to take the CPA test. The path to becoming a CPA, as you can gather, begins with your formal education. It continues with you gaining experience, studying, and developing your sharp test taking skills.
The exam is administered by the AICPA. It has four parts:
- Auditing and Attestation
- Business Environment and Concepts
- Financial Accounting and Reporting
- Regulation
You will find the CPA exam to be the same in every U.S. state. The questions you encounter will include multiple choice, simulation, and written communication. As a soon to be CPA, when you meet all of the required measures, and you pass the CPA test, you can claim the professional title. You will find the required measures vary by U.S. state. To maintain your CPA licensure, you must earn CPE credits. You must also renew your license every period.
WHAT IS A BOARD OF ACCOUNTANCY?
Did you know that every state in the U.S. has its own Board of Accountancy? The board, you will find, drives the standards for licensure for CPAs and other accounting professionals. Thanks to the Uniform Accountancy Act, you will find many standards are universal to other Boards of Accountancy across the U.S. But, you will see that each Board can set its own standards. These, you will find, can be for education, exam, and experience, to an extent. It will be smart for you to consult with your state’s State Accountancy Board to determine the below:
- Which classes count toward the 150 credit hour minimum required for you to sit for the CPA exam
- Other qualifications you must meet to sit for the exam
- Unique stipulations you may come across for meeting experiential requirements
ACCOUNTING SCHOLARSHIPS
- AICPA – Accountemps Student Scholarship. $10,000, deadline: March 1. Applicants must demonstrate financial need.
- Frank L Greathouse Government Accounting Scholarship. $10,000, deadline: Jan 6. This scholarship goes to undergrad or grad students enrolled in full time study preparing for a career in state and local gov’t finance.
- Minorities in Government Finance Scholarship. $10,000, deadline: Jan 6. This scholarship goes to an undergrad or grad student in select areas of gov’t finance. Accounting is one area. Applicants must be a member of a minority group.
- NJSCPA College Scholarship. $6,000, deadline: Jan 8. The NJSCPA offers 20 awards each year. Undergrad and grad students may be eligible.
- AICPA John L. Carey Scholarship. $5,000, deadline: March 1. The goal is to give financial help to liberal arts and non business degree holders seeking to study accounting. They must be pursuing both graduate studies in accounting and CPA licensure.
- Laurels Fund Accounting Scholarship. $5,000, deadline: May 15. This is based on academic achievement and financial need. Plus, service – applicants must have made a difference through volunteering.
- AICPA Scholarship for Minority Accounting Students. $5,000, deadline: March 1. The goal is to promote accounting as a major and career path for minority students. Applicants must show financial need.
- Advancing Women in Accounting Scholarship. $4,000, deadline: April 1. This scholarship awards women in Illinois who are preparing to become CPAs. You must plan to sit the CPA exam within three years.
- Accenture American Indian Undergraduate Scholarship. $2,500, deadline: July 15, 2020. This scholarship awards American Indian students who show leadership and academic achievement.
- Transfer Accounting Student Scholarship. $1,000, deadline: March 1. The scholarship is aimed at those planning to transfer from a two year school to study accounting in a Bachelor’s degree program.