PhD vs PsyD
What’s the Difference Between a PhD in Psychology and a PsyD? Let Us Help You Get Matched For FREE!
Table of Contents
Doctoral Degrees in Psychology
A doctoral degree in psychology can open doors to a range of career paths that often require this level of qualification, especially in fields such as clinical, counseling, and school psychology. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) forecasts a 7% growth in demand for these roles from 2023 to 2033. When considering your options, it’s essential to understand the distinctions between two primary psychology doctorate programs: the PhD in psychology and the Doctor of Psychology or PsyD. Evaluating these choices with your aspirations and interests in mind will guide you toward the most suitable path for your future.
What Is a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Psychology?
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, in psychology is inherently a research-oriented degree, emphasizing a more scholarly approach rather than a hands-on engagement with psychology practices.
Termed the “scientist-practitioner model,” this type of training focuses on inquiry, statistical analysis, testing, and data interpretation instead of clinical work. PhD programs in psychology are characterized by their comprehensive scope, covering a wide array of theories and research methodologies while allowing students to delve deeply into a chosen research area.
While honing skills in experimental design, you’ll also explore various methods of data collection, analysis, and the art of presenting findings scientifically. The pinnacle of a PhD program is the dissertation, an original theory that you defend before peers and educators with substantial evidence.
The expertise cultivated through a PhD often revolves around analytical prowess, which can be advantageous for careers like research, education, consultancy, and program evaluation. Given the breadth of psychological domains, it’s essential to pinpoint your area of interest as a prospective PhD student, ensuring alignment with faculty expertise and program offerings in fields such as PTSD, forensics, couples therapy, addiction, and beyond.
What Is a Doctor of Psychology (PsyD)?
A PsyD, known as a Doctor of Psychology, is inherently centered around the clinical practice of psychology.
Referred to as the “practitioner-scholar model,” this educational approach is distinguished by its emphasis on the direct application of research findings to therapeutic interactions with clients. As a result, PsyD programs are predominantly pragmatic in nature, featuring fewer research or statistical courses and a greater focus on clinical subject matter.
These areas delve into theories of human growth and behavior, along with techniques for assessment, diagnosis, counseling, and intervention with individuals and groups. The PsyD journey often involves specialization in a specific clinical domain, enabling you to concentrate on particular groups or issues such as troubled adolescents, families, couples, or mental health concerns. Practical experience is paramount, including immersive training within a chosen setting.
Throughout the PsyD program, you’ll encounter assessments that validate the integration of acquired skills and knowledge. Beyond accumulating clinical hours, a thesis—distinct from a PhD dissertation—is required. This PsyD paper could manifest as a lengthy essay or project. Unlike the PhD track, the emphasis lies in applying existing knowledge rather than formulating novel theories.
Regarding clinical hours, they typically comprise two components: an initial practicum phase followed by an internship during the final two semesters of the program.
PsyD vs PhD in Psychology
| Degree comparisons | PhD in Psychology | PsyD (Doctor of Psychology) |
|---|---|---|
| Who is it ideal for? | Designed for those interested in clinical practice, research and academia | Designed for those interested in clinical practice with clients |
| What does it focus on? | Focus on research | Focus on clinical (hands on) |
| What are the admission criteria? | Typical Admission criteria/requirements: Bachelors (major in psychology preferred) and or masters (preferred), strong research interests, acceptable GPA (3.0 – 3.5) and standardized test scores like the GRE, references, goals statement and writing sample. Often, there is an interview too. | Typical Admission criteria/requirements: Bachelors (major in psychology preferred) and or masters (major in the same field), CV, acceptable GPA (3.0 – 3.5) and standardized test scores like the GRE, references, goals statement, and aptitude to help others. Often, there is an interview too. |
| What can of funding can you get? | Funding: Many PhD programs offer funding as students may serve as Research Assistants or Teaching Assistants. | Funding: There may be fewer options from schools based on the premise that you earn your degree sooner and pursue a career. |
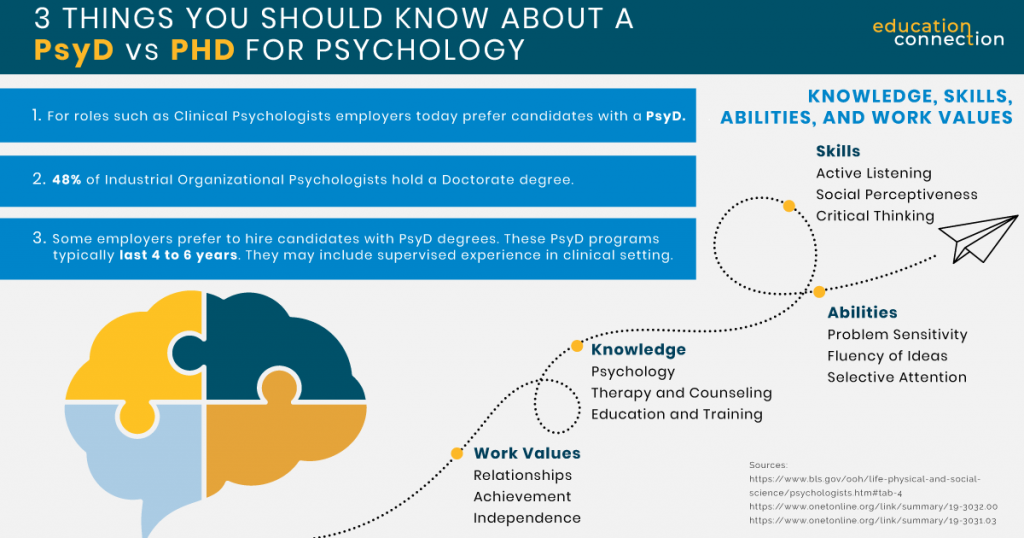
| What are the program lengths? | Program length: 5-8 years | Program length: 4–6 years |
| What do courses and training look like? | Courses: Research, statistics, analysis and theory (practical psychology knowledge) along with a research or teaching practicum and final dissertation | Courses: Direct application of psychology through courses in topics that relate to intervention and treatment methods that relate to working with clients and patients plus a one year internship |
| What are your career path options? | Career path options: Scientific researcher, educator, consultant, program director, licensed psychologist | Career path options: Licensed clinical, counseling or school psychologist (with many focal areas such as family and couple therapy) |
Which degree is perfect for you?
Regardless of the degree path you choose whether it’s a PhD or a PsyD, both can lead to licensure and open doors to similar roles within clinical psychology.
Consider your aspirations: Do you envision delving into research and academia, teaching psychology at an advanced level? Or do you picture yourself in a clinical setting, working closely with patients to help them achieve their goals?
Opting for a PhD in psychology means immersing yourself in the scientific study of behavior. This involves elements like testing, theory development, and in-depth analysis. If your ambition is to influence the field as an educator, researcher, consultant, or scholar, a PhD might align well with your goals.
On the flip side, a PsyD program focuses on the practical application of psychological science in real-world scenarios. It takes proven behavioral theories and employs them to aid individuals in overcoming challenges. If you see yourself in a counseling role, conducting one-on-one sessions or leading group therapy, a PsyD could be a suitable choice. Staying current with the latest techniques would remain essential, but your focus might lean more towards patient interaction than laboratory research.
Admission Requirements for PhD vs PsyD Programs
Admission prerequisites for PhD and PsyD programs exhibit variations among institutions, while the application process typically adheres to a uniform structure of submission and interviews.
Universities establish their distinct entry criteria, commonly emphasizing a minimum GPA and standardized test scores. Although these benchmarks are prevalent, there might be supplementary requisites. Both program types generally favor candidates with an undergraduate degree in psychology, and many also seek applicants with a master’s degree. PsyD programs often accept majors in related fields.
An expected GPA range of 3.0 and higher is widespread. Recent GRE scores may be obligatory, accompanied by their own acceptable ranges.
Admission committees meticulously assess personal statements and recommendation letters. These documents provide insights into your personality, work ethics, and alignment with the institution’s ethos.
Furthermore, there are discernible variations in the evaluated criteria for each program. PhD programs conduct more extensive assessments, considering traits like determination to excel in a rigorous PhD curriculum. They also evaluate whether your research interests correspond with faculty expertise, as successful candidates frequently engage in collaborative research ventures.
And, they look at whether your research interests align with theirs. This is to see if there’s a “fit,” as successful candidates work under faculty in their labs.
Conversely, PsyD programs concentrate on evaluating your suitability for effectively working with individuals and families dealing with diverse challenges.
What are your prospects for securing admission to a PhD or PsyD program? Intriguing data exists on this subject. According to the APA, both program types uphold higher admission standards compared to master’s in psychology programs.
At the doctoral level, clinical psychology exhibits the highest count of programs, applications, and acceptances. However, the overall acceptance rate stands at 13%. Acceptance rates for doctoral programs vary between 7% and 14% across most subfields, with significantly higher rates for school psychology (31%) and other applied psychology (25%). While almost four out of five (78%) applications to other psychology subfield programs are accepted, the limited number of programs (5) hampers comprehensive analysis.
Funding for PhD vs PsyD Programs
Another distinct contrast between PhD and PsyD programs lies in the potential funding options available to students.
Numerous PhD psychology programs provide stipends and tuition waivers. In return, students often work as research or teaching assistants, contributing to faculty projects. With a substantial stipend, students might even secure a comprehensive financial package.
PsyD students might also qualify for a stipend if the institution offers one. However, not all PsyD programs provide stipends, and tuition waivers are less common. The underlying assumption is that PsyD graduates enter the workforce sooner than PhD counterparts, leading to quicker career launches.
In cases where financial aid remains a concern, avenues might exist to fund your dissertation or thesis. According to the APA, potential sources encompass educational institutions, foundations, APA divisions and grants, psychology associations, as well as state and federal agencies.
Additionally, scholarships or fellowships could potentially reduce the overall cost of your degree. These awards might cover a portion or the entirety of your academic expenses, and unlike loans, they generally do not require repayment. Keep in mind, however, that certain conditions and terms might still apply.
Program Length in a PhD vs PsyD Program
Both a PhD and PsyD entail a significant amount of time. Many PhD programs devote about three years to course work and lab rotations. Once you compete these components, there is an exam.
Passing the exam allows you to move onto your own research project (dissertation). There may also be an option to take part in a teaching practicum, depending on the school.
To complete all these steps, you might need an average of 5 to 7 years. At that, some schools are flexible, and give more time since the research process is extensive.
In comparison, PsyD students may need from 4 to 6 years. The first three years tend to be for classes and exams. And the latter part, for practicum, internship and doctoral project. As the project is one of applied research, it may be less complex an effort than for the PhD.
Courses for a PhD vs PsyD Program
While there are places of overlap, courses for a PhD and PsyD differ, as you might guess.
A PsyD aims to provide academic, practicum, internship and research experience. While science based, it emphasizes therapy and counseling methods.
This yields a study plan around quality clinical skills. Ones needed to assess, diagnose, and treat mental health problems and illnesses. You tend to also study ethical codes and how to set boundaries with patients. So, some classes cover group dynamics, cultural diversity and other professional issues.
In some PsyD programs, you can choose a focal area as well. Forensics, health, mental illness, family, and couple are a few. Each one brings with it some electives, practicum and research. So aside from the core program, you are likely to develop expertise in one subject area.
PsyD Sample Classes
- Interviewing assessment
- Intelligence testing
- Psychoanalytic theory
- Human growth (child, adolescent, adult, older adult)
- Consultation and supervision
- Psychopharmacology
- Human sexuality
- Substance abuse
- Clinical practicum
- Statistics
- Doctoral project courses
Main goal: To learn how to provide psychological services
Central elements: Core classes, exam, electives, doctoral project courses, internship
Credits: Varies, some programs cover 70 to 80 credits
PhD programs include core courses, seminars, reading and research. Core courses frame theories like social learning, behaviorist, cognitive, gender, and more. You also tend to human growth, milestones and phases.
Research methods are central too. Topics like statistics, experiment design, and data analysis. These take a good part of your study plan and may involve lab rotations.
If you plan to teach, you might take classes that outline teaching skills. Things like how to communicate and manage a classroom. You tend to have a teaching practicum too.
Most students also choose to earn a PhD in a specific area of psychology. It guides your dissertation work and includes electives in your chosen area. For example, let’s say you do a PhD in social psychology. It may discuss all the above and add topics related to memory, attention, schema theory and social influence.
PhD in Psychology Sample Classes
- Psychology themes and theories
- Human growth (child, adolescent, adult, older adult)
- Culture and psychology
- Teaching of psychology
- Consultation
- Program assessment
- Research foundations
- Advanced qualitative reasoning
- Research theory, design, methods
- Advanced quantitative reasoning
- Research or teaching practicum
Main goal: To generate new knowledge through scientific inquiry
Central elements: Core classes, doctoral writing, research classes, dissertation support classes, teaching or research practicum
Credits: Varies, some programs cover 60 to 70 credits.
APA Accreditation
Beyond the above, APA accredited programs follow guidelines. APA accreditation promotes unified standards both for training and education.
The APA commission accredits PhD and PsyD programs in a few areas: clinical psychology, counseling psychology, school psychology, and other related areas.
APA standards also span a broad and general training in scientific psychology and core elements of practice. And aim to ready students for the practice of professional psychology.
As a graduate of an APA accredited program, you may be prepared for licensure. For one, these programs cover material you need to master for the EPPP exam. The EPPP is the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology.
It is from the Association of State and Provincial Psychology Boards (ASPPB). You need to pass this to be a licensed psychologist. Second, some states mandate you have a degree from an APA accredited program. Or prove their program is equal. In other words, if your goal is licensure, APA accreditation matters.
Potential Career Path Options for a PhD vs PsyD Program
To call yourself a licensed psychologist, you first need to take and pass the EPPP exam, or Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology. It is available through the Association of State and Provincial Psychology Boards (ASPPB). Each state may also mandate continued education to keep your license active.
Some licensed psychologists go an extra step to board certify in a specialty area. This is through the American Board of Professional Psychology (ABPP). Either a PsyD or PhD may help ready you to take the EPPP exam. But each type of degree helps you hone certain skills that may be useful in different career paths.
A PhD, for example, nurtures skills in analysis. So, it may be helpful for positions such as researcher, consultant, program director and or, educator. According to the O’NET, college psychology teachers earn median annual wages of $78,810. Demand is high too, with 5% to 8% more jobs forecast for 2022-2023. So, this may be one option.
If you prefer to solve problems in the workplace, I / O psychology is another in demand sector. Industrial organizational psychologists rely on data and earn a median annual salary of $147,420 per year.
On the other hand, a PsyD expands practical clinical skills. And these are crucial if you want to work with clients in an office or health care setting.
According to the BLS.gov, psychologists earn a median annual wage of $92,740. Many work in private practice. And others may find jobs in government, hospitals, ambulatory care, and schools. Prospects are even better if you work with seniors and rehab psychology.
Other Doctoral Degrees in Psychology
There are a few other doctoral degrees that may be useful if you want to pursue a career in psychology. One is the EdS, or Education Specialist, and another is a DBA, or Doctor of Business Administration (likely in organizational psychology).
Education Specialist (EdS)
An EdS is a post masters and pre doctoral degree. It generally takes about three years to complete after a masters degree. Most EdS programs are designed for professionals who would like to study beyond the master’s degree level but do not plan to pursue a doctoral degree like the PhD or PsyD.
The coursework is at the advanced graduate level though. So many schools will transfer earned credits to a doctoral degree if you decide to pursue one later.
Some students choose the EdS to improve their skills for advanced licensure in K – 12 related roles or to prep for academic and administrative leadership roles within higher education.
In some states, graduates can pursue licensure with an EdS. In other states, however, you must have either a PhD or EdD (a doctoral level degree) to pursue licensure.
Both school counseling and school psychology are practice areas in EdS programs. School psychology programs cover education and mental health subject areas such as behavioral and learning disorders, performance plans, and specific counseling tactics for students.
If you want to prepare for a career as a school psychologist, this may be an option. According to the BLS, the demand for school psychologists is on the rise. Apart from 7% more jobs by 2023-2033, average annual salaries are about $92,740.
Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
A DBA in I/O psychology studies human behavior in the workplace. It typically takes about three years to complete after a masters or MBA. Many DBA programs are for senior executives who make decisions and policies for their business. For instance, human resource directors and training managers.
These roles tend to rely on research and data to solve problems. In a work setting, these problems often affect productivity, profit, morale and performance. Some of the subject areas in a DBA program are leadership and coaching. You may also learn how to manage conflict and group dynamics.
As a doctorate in business admin, it is likely to focus on managerial theory too. So, tactics, planning and policy processes tend to be key topics also. Some I/O psychologists launch a career with a masters in I/O psychology. And if a career as a licensed psychologist is your goal, a PhD may be more useful.
At present, the Society for Industrial Organizational Psychology (SIOP) does not list the DBA as a path to licensure. You would need either a PhD or PsyD from an accredited school and then undergo a supervised practice and pass the EPPP exam.
But if a C suite job lines up with your personality, a DBA may provide other possible paths. Consulting is one area where demand is high. Business consultants use psychological research methods as well as strategic managerial skills. They can help a company become more efficient and control costs.
According to the BLS, jobs for consultants are on the rise by 11% through 2033. Other job titles are management analyst and leadership development manager. Beyond faster than average growth, consultants earn an average annual salary of $99,410. And some earn more than $172,280.
Financial Aid Info
- Your Guide to Federal Student Loans
- Grants and Scholarships
- Military Benefits
- Private Student Loans
- Repaying Student Loans
- Student Loan Consolidation
- Education Tax Credits | AOTC & LLC
- 15 Military Scholarships to Apply For in 2023
- Grad School Scholarships
- 12 Graduate Scholarships for DACA Students in 2025
- Graduate Scholarships for International Students
- Grants for Women
- Guide Schools & Scholarships for Students with Disabilities
- Guide Tribal Colleges and Scholarships for Native Americans
- 8 Adult Scholarships for Adults Returning to School
- How to Earn Credit for College with Life Experience
- The Psychology of Lying
- 36 Companies That Pay For College
- FAFSA: Parent and Student Assets
- How Do You Get Student Loans Without a Job?

